Embedded finance integrates payments, lending, and banking directly into everyday apps, enabling seamless user experiences, faster transactions, improved accessibility, and new revenue models for businesses while reshaping digital platforms into full-service financial ecosystems globally at scale.
Embedded finance represents one of the most significant paradigm shifts in financial technology. In today’s digital-first economy, consumers and businesses alike expect seamless, personalized experiences that integrate finance directly into their workflows. From paying for a ride without ever opening a separate wallet app to accessing a loan right at the point of sale, embedded finance eliminates friction by weaving financial services—such as payments, lending, insurance, and banking—into the digital products and platforms people use every day. This integration not only enhances user satisfaction but also unlocks new revenue streams and data insights for businesses. As a rising star in fintech innovation, embedded finance is powering next-generation experiences across industries, enabling companies to differentiate their offerings and deepen customer loyalty. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the evolution, benefits, and real-world applications of embedded finance, examine the underlying technologies and regulatory considerations, and offer best practices for successful implementation and future growth.
What is Embedded Finance and Why It Matters?
Embedded finance puts financial services directly into apps people use every day. Users don’t need to switch to a separate bank or payment app. They can pay for rides, shop online, or manage expenses on the same platform.
This idea came from open banking and API-driven systems. Banks and fintech companies can offer services like payments, loans, and identity verification through secure APIs. Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) platforms make it easier by providing ready-to-use banking infrastructure and compliance tools.
Today, embedded finance combines technology and banking. It lets businesses provide smooth, in-app financial experiences. Users get convenience, and companies get more engagement and loyalty.
The Evolution of Embedded Finance
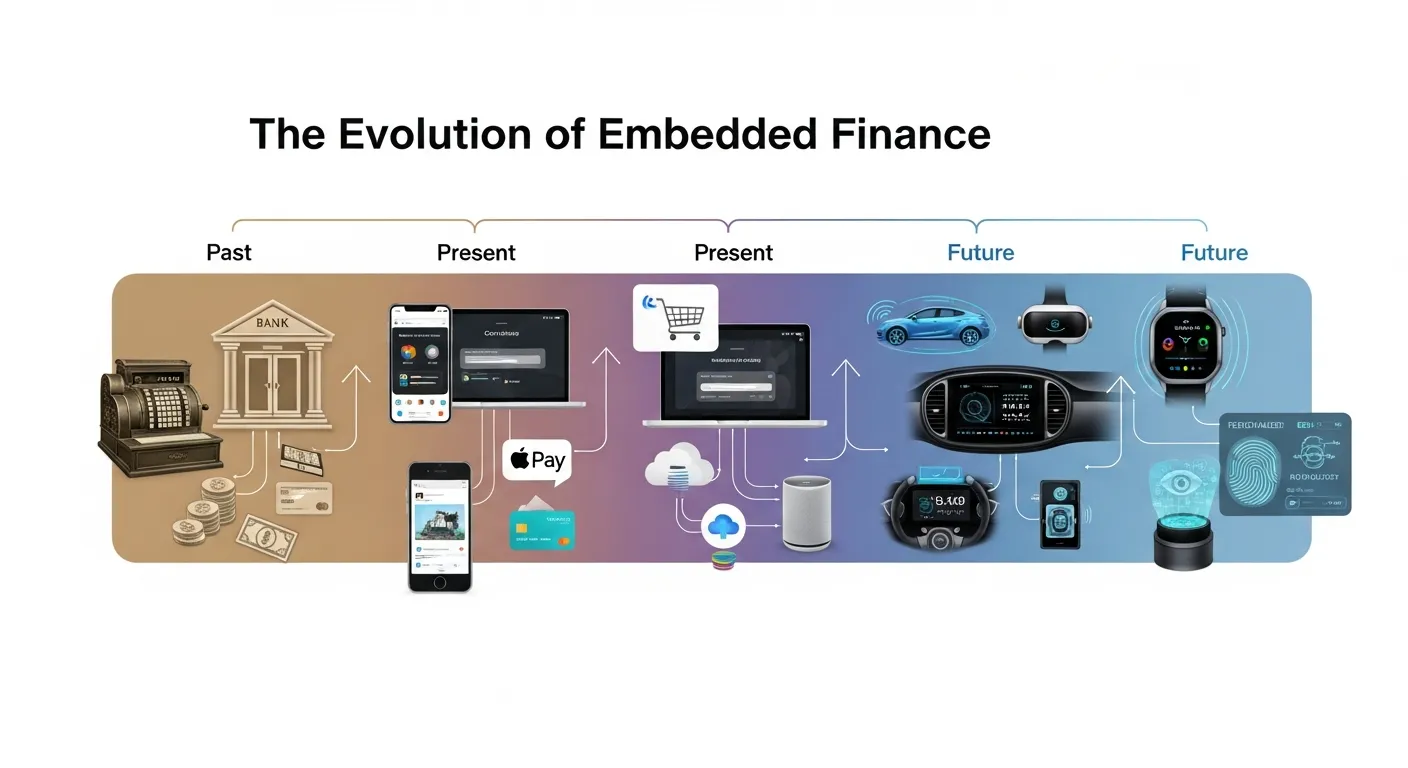
Embedded finance did not emerge overnight—it evolved alongside digital transformation, open banking, and API-driven innovation. As consumers shifted toward mobile-first and platform-centric experiences, traditional banking models struggled to keep pace. Embedded finance filled this gap by allowing financial services to move closer to the point of need, transforming everyday digital interactions into financial touchpoints without disrupting user flow.
Over time, this evolution has reshaped expectations around how and where financial services should exist. Instead of standalone banking products, users now expect finance to be invisible, contextual, and instantly accessible. This shift marks a fundamental change in how value is delivered within digital ecosystems.
Key Benefits
- Frictionless User Experience: Users enjoy uninterrupted workflows, reducing drop-off rates and improving conversion by eliminating redirects to external financial apps.
- New Revenue Streams: Companies can monetize payment flows, lending fees, and premium financial services, diversifying income beyond core product offerings.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: Personalized financial solutions—such as in-app credit or real-time insurance—strengthen brand affinity and encourage repeat engagement.
- Data-Driven Insights: Integrating finance natively captures valuable data on spending patterns, credit behavior, and transaction volumes, informing more targeted marketing and product development.
- Competitive Differentiation: Early adopters can distinguish themselves in crowded markets by delivering unique, value-added financial experiences tailored to their audience.
Why Embedded Finance Is Accelerating Globally
The rapid global adoption of embedded finance is driven by changing consumer behavior, mobile penetration, and the rise of digital platforms. Users increasingly prefer speed, convenience, and personalization, while businesses seek scalable revenue models and deeper engagement. Embedded finance satisfies both needs by seamlessly aligning financial services with daily digital activities.
Additionally, emerging markets are adopting embedded finance at an accelerated pace due to limited traditional banking access. By integrating financial services into widely used apps, platforms can promote financial inclusion, expand access to credit, and support underserved populations at scale.
Real-World Use Cases
- E-Commerce Platforms: Integrate “Buy Now, Pay Later” and one-click checkout options directly in their shopping carts, boosting average order values and customer satisfaction.
- Ride-Sharing and Mobility Apps: Embed payments, tipping, and driver financing into the trip flow, streamlining the experience for riders and drivers alike.
- SaaS and Workflow Tools: Include invoicing, expense management, and payroll disbursements within their interfaces, reducing the need for multiple systems.
- Gig Economy Marketplaces: Offer on-demand payouts and micro-loans to freelancers, helping them manage cash flow between assignments.
- Travel and Hospitality Booking Sites: Provide instant travel insurance, currency exchange, and loyalty points redemption at checkout.
- Healthcare Portals: Embed patient billing, payment plans, and health savings accounts to simplify medical payments and improve transparency.
Success Stories: Real-World Case Studies
Shopify and Stripe: E-commerce giant Shopify partnered with payments provider Stripe to embed multi-currency checkout, fraud detection, and capital lending directly within its merchant dashboard. This integration reduced complexities for merchants, increased transaction volumes by over 20%, and generated new financing revenue streams.
Uber’s In-App Wallet: Uber introduced a digital wallet within its app, enabling riders to top up balances, pay for rides seamlessly, and earn rewards. Drivers also gained access to instant payouts and vehicle financing options, improving driver retention and operational efficiency.
Square’s Seller Financing: Point-of-sale (POS) provider Square embedded a merchant cash advance product—Square Capital—into its dashboard, allowing businesses to apply for and receive funds in minutes. This seamless lending solution has disbursed billions in capital and helped many small merchants weather cash flow challenges.
Grab PayLater in Southeast Asia: Super-app Grab launched PayLater, an embedded lending solution that offers short-term credit at checkout across ride-hailing, food delivery, and retail services. Grab reported a 30% uplift in order frequency and deeper engagement across its ecosystem.
Technology Behind Embedded Finance
APIs and Webhooks: Secure, well-documented APIs enable real-time data exchange between financial institutions and embedded platforms, while webhooks send event-driven notifications.
Banking-as-a-Service Platforms: BaaS providers manage regulatory compliance, core ledger systems, and settlement processes, exposing modular financial products through developer portals.
Microservices Architecture: Decomposed services for payments, identity verification, and compliance can be independently deployed and scaled, accelerating development and resilience.
Cloud Infrastructure: Scalable, cloud-native environments host critical services, handle peak transaction volumes, and facilitate rapid iterations.
Security and Compliance Tooling: Encryption, tokenization, and continuous security monitoring protect sensitive data, while built-in compliance frameworks automate KYC/AML checks.
Challenges and Risks
Despite its benefits, embedded finance presents challenges, including regulatory complexity, data privacy and cybersecurity risks, vendor and third-party reliance, integration hurdles with legacy systems, and the need for clear liability and risk allocation agreements. Addressing these challenges requires robust compliance frameworks, thorough vendor due diligence, and a proactive approach to security and incident response.
Regulatory Considerations
Embedded finance operates in a heavily regulated environment. Key considerations include licensing and authorization for services like payments and lending, rigorous KYC and AML compliance procedures, transparent consumer protection disclosures, and careful management of cross-border rules such as currency controls and tax obligations.
How Businesses Can Implement Embedded Finance
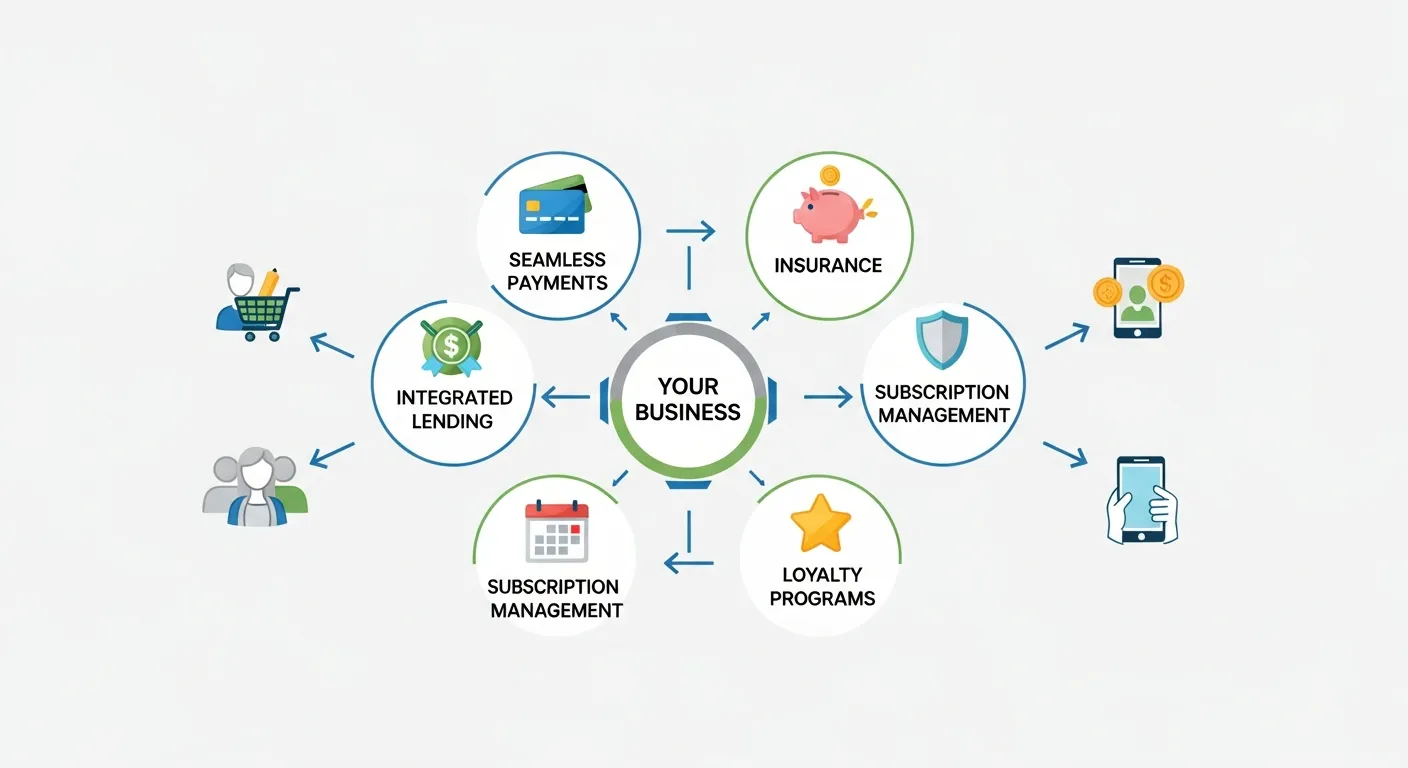
- Identify Strategic Objectives: Determine how embedded finance aligns with your business goals, whether it’s improving conversion, increasing loyalty, or generating new revenue.
- Select the Right Partner: Evaluate BaaS providers and fintech platforms based on product capabilities, regulatory coverage, API quality, security certifications, and support resources.
- Design Customer Journeys: Map out seamless user flows for onboarding, payments, lending, or insurance that maintain a unified brand experience.
- Develop and Test Integrations: Use sandbox environments to integrate APIs, SDKs, and webhooks. Conduct end-to-end testing for reliability and performance under load.
- Establish Compliance Controls: Work with legal and compliance teams to embed KYC/AML procedures, data privacy safeguards, and transparent disclosures within your product.
- Launch and Iterate: Roll out embedded finance features to a pilot segment, gather user feedback, and refine functionality before full-scale deployment.
- Monitor Performance: Continuously track key metrics such as transaction volume, approval rates, and customer satisfaction to optimize offerings and mitigate risks.
Embedded Finance and Financial Inclusion
Embedded finance plays a critical role in advancing financial inclusion by reaching users who may not have access to traditional banking infrastructure. Through mobile apps and digital platforms, individuals and small businesses can access payments, savings, and credit without complex onboarding or physical branch visits.
This inclusive approach empowers gig workers, freelancers, and small merchants to participate more fully in the digital economy. By lowering entry barriers, embedded finance helps bridge financial gaps and supports sustainable economic growth across diverse regions.
Key Metrics to Track
- Transaction Volume and Value: Measure the number and total value of transactions processed through your embedded financial services.
- Approval and Decline Rates: Monitor loan or credit application acceptance and rejection rates to fine-tune underwriting criteria.
- Cart Abandonment: Analyze exit rates at payment or financing steps to identify friction points.
- Revenue Attribution: Attribute fees, interest, and ancillary income generated by embedded services to assess ROI.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Evaluate the impact of embedded finance on long-term customer engagement and profitability.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Gather feedback on the user experience to drive improvements and trust.
The Role of User Trust in Embedded Finance Adoption
Trust is a foundational element in the success of embedded finance solutions. Users are more likely to adopt in-app financial services when platforms demonstrate transparency, reliability, and strong data protection practices. Clear communication around fees, terms, and security measures significantly influences user confidence.
In addition, influencer credibility and expert endorsements play a growing role in building trust for embedded finance offerings. When trusted fintech influencers, industry experts, or digital creators explain and validate in-app financial features, users feel more confident trying new services.
As financial services become embedded into non-financial platforms, maintaining consistent branding, dependable customer support, and authentic influencer advocacy becomes essential. Platforms that combine trust-building measures with influencer-driven education can accelerate adoption, reduce churn, and strengthen long-term user relationships.
Best Practices for Building Trust
Successful embedded finance initiatives hinge on building customer trust through transparent communication of fees and terms, consistent branding, user education materials, dedicated customer support channels, and visible security certifications such as PCI DSS and ISO 27001 to reassure users about data protection standards.
Future Trends in Embedded Finance
As embedded finance continues to evolve, key trends include AI-powered personalization for tailored financial recommendations, blockchain and smart contracts for transparent cross-border settlements, real-time payments infrastructure for instant liquidity, platform banking offering end-to-end financial services within non-financial apps, and sustainable finance products that align with ESG goals.
Embedded Finance as a Catalyst for Digital Transformation

Embedded finance is not just a financial innovation—it is a catalyst for broader digital transformation. By integrating finance into core user journeys, businesses can redesign workflows, optimize operations, and unlock new strategic capabilities. This integration enables faster decision-making, automation, and real-time insights across platforms.
As digital transformation accelerates across industries, embedded finance will continue to play a central role in shaping how platforms scale and compete. Organizations that embrace this shift early can future-proof their offerings and remain resilient in an increasingly digital economy.
Conclusion
Embedded finance is changing the way people and businesses manage money. It provides seamless, in-app financial experiences that boost engagement and create new revenue opportunities. By following regulatory compliance, prioritizing data security, and partnering with trusted Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) providers, companies can embed financial services directly into their platforms. Staying updated on fintech innovations, digital payment trends, and consumer expectations is essential for long-term growth. Adopting embedded finance allows businesses to offer frictionless, personalized financial solutions, enhance customer satisfaction, and remain at the forefront of financial technology innovation.
FAQs: Financial Services in Everyday Apps
What is integrated financial technology?
Integrated financial technology brings services like payments, lending, and banking directly into non-financial apps or digital platforms, allowing users to access money-related features without leaving the app.
How do in-app financial services work?
These services work through APIs, open banking frameworks, and partnerships between banks, fintech providers, and platforms, enabling apps to offer regulated financial features without becoming banks.
Why are in-app financial services important?
They reduce friction, increase convenience, and create smoother digital experiences while helping businesses improve engagement, efficiency, and customer retention.
What are common examples of in-app financial services?
Examples include one-click payments, buy-now-pay-later options, digital wallets, instant seller payouts, in-app insurance, and integrated lending solutions.
Which industries benefit most from in-app financial services?
E-commerce, fintech platforms, mobility services, SaaS tools, healthcare portals, logistics providers, and digital marketplaces benefit significantly from these integrations.
How do integrated financial tools improve customer experience?
By enabling faster checkouts, real-time transactions, and personalized financial options, these tools eliminate extra steps and create seamless user journeys.
Are in-app financial services secure?
Yes, when supported by regulatory compliance, strong encryption, fraud prevention systems, and continuous transaction monitoring, these services remain highly secure.
What role do APIs play in digital financial integration?
APIs serve as the core technology layer, securely connecting apps with banks and fintech providers for real-time payments, data sharing, and financial operations.
How do platforms generate revenue from financial integrations?
Revenue comes from transaction fees, interest from lending products, subscriptions, and value-added financial features offered within digital platforms.
Can small businesses use integrated financial solutions?
Yes, small and medium-sized businesses can access payments, instant settlements, lending, and cash-flow tools directly within the software platforms they already use.
How are integrated financial services different from traditional banking?
Traditional banking operates through standalone channels, while modern financial integrations deliver services directly inside everyday apps and digital workflows.
What is the future of in-app financial integration?
The future includes platform-based economies, super apps, real-time payments, and fully connected digital financial ecosystems driven by API-led innovation.








The Future of Personal Finance: Autonomous Finance and AI Money Management
The Role of AI in Digital Financial Decision Making
What is a Fintech Company?
What is a Fintech Firm? Everything You Need to Know
Digital Twin Technology in Finance: How Virtual Models Are Transforming Risk Management
The Future of Personal Finance: Autonomous Finance and AI Money Management
AI Credit Scoring: Revolutionizing SME Banking and Digital Loans
AI Fraud Detection: How Banks Prevent Financial Crime in Real Time