Digital Identity Verification is transforming finance onboarding by enabling fast, secure, and compliant customer verification through digital channels. By replacing manual checks with AI, biometrics, and real-time data validation, financial institutions can reduce fraud, improve customer experience, and meet strict regulatory requirements. As digital finance continues to scale globally, robust Digital Identity Verification solutions are becoming essential for seamless onboarding, risk management, and long-term trust in financial ecosystems.
Financial institutions are racing to provide seamless customer experiences while ensuring robust security and compliance. Traditional onboarding methods, which often rely on manual document checks and in-person verification, can be time-consuming, error-prone, and expensive. Enter digital identity verification (IDV): a transformative solution that leverages cutting-edge technologies, including artificial intelligence, biometrics, and blockchain, to automate and secure the onboarding process. By validating user identities in real time, digital IDV not only improves customer satisfaction but also mitigates fraud, accelerates growth, and helps financial firms comply with ever-evolving regulations. In this comprehensive guide, we examine the fundamental concepts, technologies, advantages, challenges, and emerging trends in digital identity verification for digital finance.
As the global digital finance sector expands, the need for scalable and reliable IDV systems has never been greater. Whether you are a challenger bank, fintech startup, or traditional financial services provider, adopting a robust digital identity framework is crucial for staying competitive in a world where trust and efficiency are paramount.
What Is Digital Identity Verification?
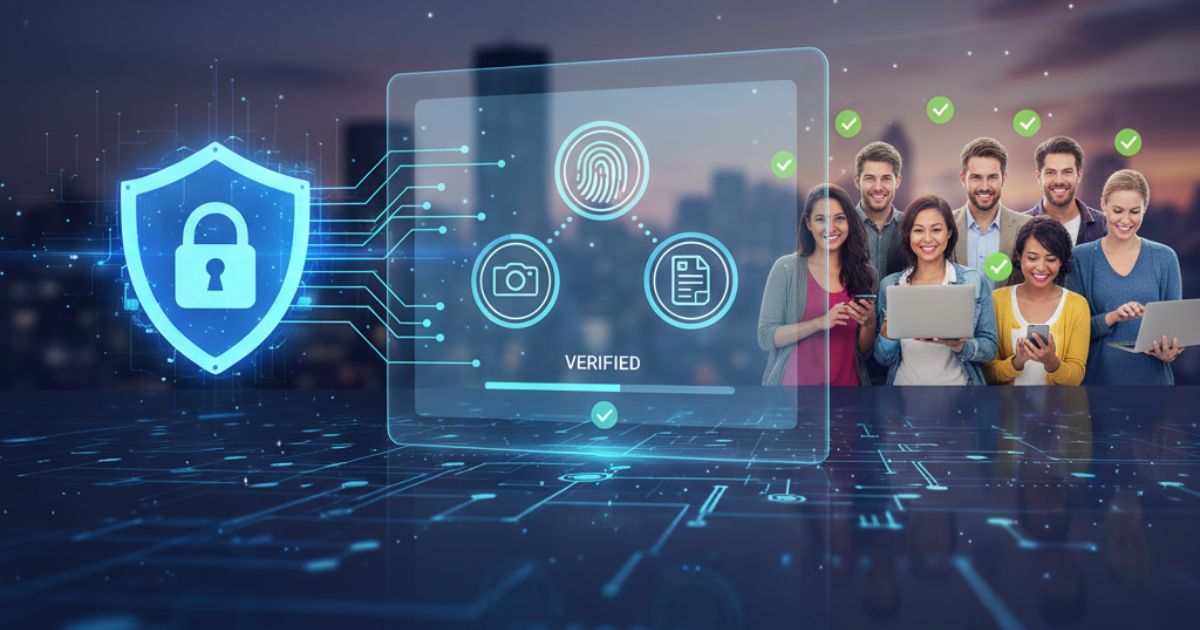

Digital identity verification (IDV) is the process of confirming an individual’s or organization’s identity using electronic and digital technologies. Instead of relying on physical documents and in-person verification, digital IDV allows users to submit identity information online. Advanced systems then verify this data in real time, helping financial institutions improve efficiency, reduce fraud, and deliver a smoother onboarding experience.
Key components of digital identity verification include:
-
Online submission of identity documents such as passports, driver’s licenses, or utility bills
-
Automated cross-checking of data against trusted and authoritative databases
-
Biometric verification, including facial recognition, fingerprints, or voice authentication
-
Device fingerprinting to assess risk based on device and network behavior
-
AI-powered automation to reduce manual intervention and human error
-
Real-time verification that completes checks in seconds or minutes
-
Improved customer experience through faster and frictionless onboarding
-
Support for ongoing monitoring, high-risk transaction verification, and regulatory reporting
-
Strong alignment with KYC, AML, and data protection requirements
Key Technologies Powering Digital IDV
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI algorithms analyze patterns in submitted documents and user behavior to detect anomalies and fraudulent attempts. ML models trained on vast datasets continuously improve their ability to distinguish between legitimate and fake credentials.
- Biometric Authentication: Facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and voice biometrics enable secure and frictionless verification. Liveness detection technology can identify spoofing attempts, ensuring that users present real, live biometric traits.
- Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology: Blockchain can provide tamper-evident audit trails for identity data, enabling secure sharing of verified information between trusted parties while preserving privacy.
- Document Verification Engines: These tools automatically extract and validate data from identity documents using Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and computer vision techniques.
- Device Fingerprinting: By collecting metadata such as IP address, device type, and browser configuration, fingerprinting systems assess the risk profile of each session, flagging suspicious activity for further review.
Together, these technologies form a robust framework that can adapt to evolving security threats and regulatory requirements in the digital finance sector.
Read Further Reading, explore Biometric Authentication: The Future of Banking Security
Benefits of Digital IDV for Customer Onboarding
Implementing digital identity verification delivers a range of strategic advantages for financial institutions:
- Enhanced User Experience: Automated checks reduce manual steps, enabling customers to open accounts and access services in minutes, not days. Mobile-first workflows support remote onboarding with minimal friction.
- Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention: Real-time identity checks, combined with biometric and behavioral analytics, help detect and prevent identity theft, account takeover, and synthetic fraud.
- Regulatory Compliance: Digital IDV platforms are designed to meet global Know your customer (KYC), AML, and data protection standards, streamlining audit trails and reporting to regulatory bodies.
- Operational Efficiency: Automation frees up staff from routine verifications, allowing teams to focus on higher-value tasks and reducing costs associated with manual processing.
- Scalability: Whether serving hundreds or millions of customers, digital IDV systems can handle high volumes without compromising accuracy or speed.
- Global Accessibility: Multi-language support and localized document checks enable institutions to quickly expand into new markets, offering a consistent onboarding experience worldwide.
For fintech startups and challenger banks that rely heavily on digital channels, these benefits translate directly into competitive differentiation. Faster onboarding leads to higher conversion rates, while robust fraud controls help reduce chargebacks and mitigate reputation risks. Moreover, by centralizing identity data in secure, compliant systems, institutions can leverage verified profiles for cross-selling, personalization, and loyalty initiatives, creating a more cohesive customer journey.
For example, a mobile-first neobank reported a 75% reduction in manual review times and a 40% increase in completed applications after integrating a digital IDV solution. Similarly, a global payment provider saw fraudulent account openings drop by over 50 percent within the first quarter of deployment, illustrating the tangible impact on both top-line growth and bottom-line protection.
Compliance and Risk Management Considerations
Financial institutions face intense regulatory scrutiny around customer due diligence and anti-money laundering controls. Digital identity verification enhances compliance efforts in several ways:
- Automated KYC/AML Checks: Integrated watchlist screening, adverse media databases, and transaction monitoring modules help automatically identify politically exposed persons (PEPs) and sanctioned individuals.
- Audit Trails and Reporting: Every IDV interaction is logged with timestamps, IP addresses, and verification results, creating an immutable record for regulators and auditors.
- Data Privacy and Security: Leading solutions utilize encryption, tokenization, and data minimization strategies to safeguard personal information in transit and at rest, enabling firms to comply with GDPR, CCPA, and other data protection laws.
- Risk Scoring and Enhanced Due Diligence: Dynamic risk scoring models assess individual customer profiles, triggering additional checks for high-risk users or transactions as required by internal policies or regulatory mandates.
By embedding compliance controls directly into the onboarding workflow, institutions can reduce the cost and complexity of managing fragmented systems while maintaining full regulatory alignment.
Real-World Case Studies

Many financial organizations have embraced digital IDV with notable success:
- Global Digital Bank: Implemented AI-driven IDV to replace manual verification, leading to a 60 percent decrease in onboarding time and a 30 percent reduction in operational costs.
- International Money Transfer Service: Leveraged biometric authentication and document verification to comply with diverse regional regulations, increasing cross-border transaction approvals by 25 percent.
- Cryptocurrency Exchange: Adopted a blockchain-backed identity registry to securely store and share verified customer data, cutting customer complaints related to account freezes by 45 percent.
These examples demonstrate how digital identity verification can be tailored to various business models, ranging from retail banking to specialized fintech services, thereby driving efficiency and fostering customer trust at scale.
Best Practices for Implementing Digital IDV
- Define Clear Requirements: Assess your business needs, customer segments, and regulatory obligations to choose a solution that aligns with your strategy.
- Prioritize User-Centric Design: Develop intuitive onboarding flows that guide users through each step, provide clear instructions, and offer real-time feedback.
- Ensure Integration Flexibility: Opt for modular platforms with APIs and SDKs that can integrate seamlessly with existing core banking systems, CRMs, and third-party services.
- Regularly Update and Train Models: Machine learning components require ongoing training with new data to maintain accuracy and detect emerging patterns of fraud.
- Monitor Performance and Metrics: Track key performance indicators, including verification turnaround time, customer drop-off rates, false positives, and fraud incidents, to optimize workflows.
- Maintain Regulatory Vigilance: Stay informed about global and local regulatory changes, updating your IDV workflows and documentation to ensure ongoing compliance.
By following these best practices, financial institutions can avoid common pitfalls, such as overbearing checks that frustrate users or underpowered systems that leave gaps in security. A phased rollout, starting with a pilot program and expanding based on feedback and performance data, can help minimize risks while maximizing user acceptance and ROI.
Challenges and How to Address Them
While digital IDV offers significant advantages, it also presents challenges:
- Data Privacy Concerns: Collecting sensitive biometric and identity data raises privacy issues. Mitigation: Implement strong encryption, data minimization, and obtain explicit user consent.
- False Positives and Negatives: Automated systems may sometimes reject genuine customers or approve fraudulent ones. Mitigation: Combine automated checks with human review for edge cases and regularly fine-tune models.
- Technology Integration: Legacy systems may not support modern APIs or data formats. Mitigation: Utilize middleware or integration layers to bridge gaps and collaborate with vendors to create customized connectors.
- Accessibility and Inclusion: Users with poor internet connectivity or limited digital literacy may struggle. Mitigation: Offer alternative verification channels, such as call centers or assisted onboarding kiosks.
Addressing these challenges proactively ensures a more resilient and inclusive onboarding system that strikes a balance between security and user accessibility.
Future Trends in Digital Identity Verification

The digital identity landscape continues to evolve, with several emerging trends poised to shape the future of onboarding in finance:
- Decentralized Identity (DID): Users control their own identity credentials, stored in decentralized wallets, which grant selective access to verifiers without revealing unnecessary personal data.
- Behavioral Biometrics: Continuous authentication using typing patterns, mouse movements, and navigation habits to detect anomalies in real time.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Cryptographic protocols that allow users to prove specific attributes (e.g., age, citizenship) without disclosing full identity details.
- Advanced AI Explainability: Transparent AI models that provide clear insights into verification decisions, improving trust and regulatory acceptance.
- Cross-Industry Identity Hubs: Shared platforms where verified identity data can be securely exchanged between banks, insurers, and telecom providers, reducing duplication of effort.
As these innovations mature, the on boarding experience will become faster, more secure, and more privacy-preserving than ever before.
Conclusion
Digital identity verification is rapidly transforming the customer on boarding process in the digital finance sector, delivering enhanced security, compliance, and a superior user experience. By leveraging AI, bio-metrics, blockchain, and device intelligence, financial institutions can streamline processes, reduce fraud, and meet stringent regulatory requirements, all while offering seamless digital journeys to customers worldwide. As part of strengthening cybersecurity in digital finance, these solutions play a crucial role in protecting sensitive data and maintaining trust. However, successful implementation requires careful planning, ongoing performance monitoring, and a commitment to data privacy and accessibility. Looking ahead, emerging technologies such as decentralised identity, behavioral biometrics, and zero-knowledge proofs will further revolutionize how we establish and trust digital identities. Institutions that embrace these advancements proactively will gain a significant competitive edge, fostering customer loyalty and unlocking new growth opportunities in an increasingly digital-first world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Digital Identity Verification in finance onboarding?
Digital Identity Verification is the process of confirming a customer’s identity using digital tools such as document verification, biometrics, and AI during finance onboarding. It enables financial institutions to verify users remotely, securely, and in real time.
2. Why is Digital Identity Verification important for finance onboarding?
Digital Identity Verification reduces onboarding friction, speeds up account opening, prevents fraud, and ensures compliance with KYC and AML regulations. It allows financial institutions to onboard customers efficiently without compromising security.
3. How does Digital Identity Verification work?
The process typically involves uploading identity documents, performing biometric checks (such as facial recognition), validating data against trusted databases, and assessing device or behavioral risk signals—all completed within minutes.
4. Which technologies are used in Digital Identity Verification?
Key technologies include artificial intelligence, machine learning, biometric authentication, document verification with OCR, device fingerprinting, and in some cases, blockchain-based identity systems.
5. How does Digital Identity Verification improve customer experience?
By automating identity checks, finance onboarding becomes faster and more convenient. Customers can open accounts remotely using mobile devices, avoiding in-person visits and lengthy manual processes.
6. Can Digital Identity Verification prevent financial fraud?
Yes. Digital Identity Verification helps detect identity theft, synthetic fraud, and account takeovers by combining real-time checks, biometrics, behavioral analysis, and risk scoring models.
7. Is Digital Identity Verification compliant with regulations?
Most modern Digital Identity Verification platforms are designed to comply with global KYC, AML, GDPR, and data protection regulations, providing audit trails and secure data handling.
8. How does Digital Identity Verification support global finance onboarding?
Digital IDV solutions support multiple languages, document types, and regional regulations, enabling financial institutions to onboard customers across borders while maintaining compliance.
9. What challenges exist in implementing Digital Identity Verification?
Common challenges include data privacy concerns, false positives or negatives, integration with legacy systems, and accessibility for digitally excluded users. These can be managed with proper design and governance.
10. Is Digital Identity Verification suitable for fintech startups and neobanks?
Yes. Fintechs and neobanks rely heavily on digital channels, making Digital Identity Verification essential for scalable, cost-effective, and secure finance onboarding.
11. How does Digital Identity Verification help with ongoing compliance?
Beyond onboarding, Digital Identity Verification supports continuous monitoring, enhanced due diligence, transaction verification, and regulatory reporting throughout the customer lifecycle.
12. What is the future of Digital Identity Verification in finance onboarding?
The future includes decentralized identity, behavioral biometrics, zero-knowledge proofs, and AI-driven decision transparency—making finance onboarding faster, safer, and more privacy-focused.







Embedded Finance and the Future of Seamless Digital Financial Services
How AI-Based Fraud Detection is Protecting Digital Payments
Harnessing AI and Machine Learning for Fraud Detection in Digital Finance
Digital Marketing for Financial Services: Strategies That Deliver Results
Digital Twin Technology in Finance: How Virtual Models Are Transforming Risk Management
The Future of Personal Finance: Autonomous Finance and AI Money Management
AI Credit Scoring: Revolutionizing SME Banking and Digital Loans
AI Fraud Detection: How Banks Prevent Financial Crime in Real Time