Traditional banking security methods like passwords, PINs, and security questions are no longer enough. Cybercriminals are getting smarter, and financial fraud is increasing every year. Because of this, banks are moving toward stronger and more reliable security solutions. One of the most effective solutions today is biometric authentication.
Biometric authentication uses unique biological traits such as fingerprints, facial features, voice patterns, and iris scans to verify identity. Unlike passwords, these biometric identifiers are difficult to steal, copy, or misuse. This makes biometric security systems a powerful tool for protecting online banking, mobile banking apps, and digital financial transactions.
In this blog, we will explore how biometric authentication is transforming banking security. You will learn about different types of biometric verification, the key benefits for banks and customers, and the challenges involved in implementation. Understanding biometric technology is essential for anyone interested in banking security, financial cybersecurity, and the future of secure digital banking.
What is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication is a modern security method that verifies identity using a person’s unique physical or behavioral traits. Instead of relying on passwords, PINs, or security questions, it uses characteristics that are part of the individual. This makes identity verification more secure and harder to fake.
Banks and financial institutions are rapidly adopting biometric security systems to protect customer accounts and digital transactions. Popular methods include fingerprint authentication, facial recognition technology, voice recognition, and iris scanning. These biometric verification methods help prevent fraud, reduce unauthorized access, and improve overall banking security.
By replacing traditional login methods, biometric authentication also improves the user experience. Customers can access their accounts faster and more conveniently while banks strengthen their digital identity verification and financial cybersecurity at the same time.
Types of Biometric Authentication in Banking
Banks use different types of biometric authentication to protect customer accounts and financial data. These biometric security methods rely on unique physical or behavioral traits to verify identity. Each type of biometric technology has its own benefits and works best in specific banking use cases, such as mobile banking apps, ATMs, and phone banking services.
Fingerprint Scanning
Fingerprint scanning is one of the most widely used biometric authentication methods in banking. Most smartphones come with built-in fingerprint sensors, which makes integration easy for mobile banking apps. Customers can log in or approve transactions quickly without entering passwords.
This method improves user experience while reducing the risk of stolen passwords or unauthorized access. Fingerprint authentication is fast, reliable, and cost-effective, making it ideal for everyday banking activities.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition uses advanced biometric software to analyze the unique structure of a person’s face. Many banking apps use this technology for secure login and identity verification. It allows users to access their accounts with a simple face scan.
Modern facial recognition systems include liveness detection. This helps prevent fraud attempts using photos or videos. As a result, facial biometrics offer strong security with high user convenience.
Eye Recognition (Iris and Retina Scanning)
Eye recognition is a highly secure biometric authentication method used in advanced banking systems. It includes iris scanning and retina scanning, both of which analyze unique patterns in the eye.
Iris recognition maps the detailed patterns of the iris, which remain stable over a lifetime. Retina scanning focuses on blood vessel patterns at the back of the eye. These methods offer very high accuracy and are often used for high-value transactions or restricted access systems.
Although eye recognition requires specialized hardware, it provides one of the strongest levels of biometric security in banking.
Voice Recognition
Voice recognition verifies user identity using unique vocal characteristics such as pitch, tone, and speech patterns. Banks widely use this form of biometric authentication in phone banking and call center security systems.
This technology reduces dependence on security questions, PINs, and password-based verification, which are easier to compromise. By using voice biometrics, banks can deliver faster and more secure identity checks during customer calls.
Voice recognition also plays a key role in voice-enabled banking, where customers can access services through natural speech. It improves banking security, enhances the customer experience, and supports seamless digital identity verification without friction.
The Benefits of Biometrics for Banking Security
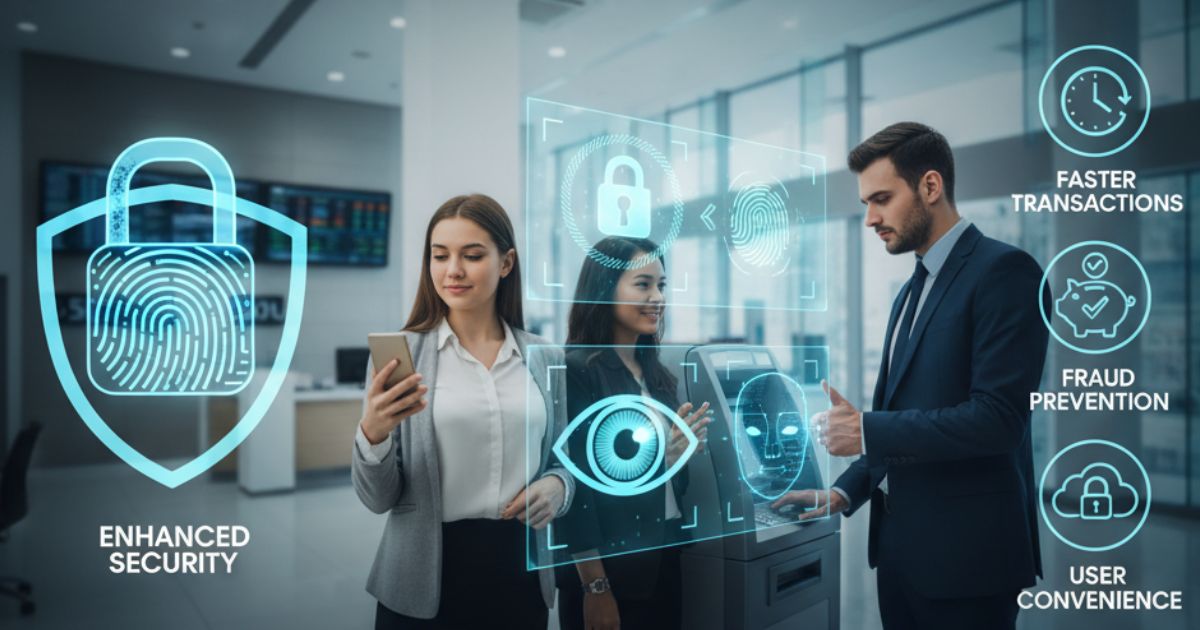

Biometric authentication is transforming banking security by offering safer and faster ways to verify customer identity. As cyber threats grow, banks are moving away from traditional passwords toward biometric security systems. These systems improve protection, enhance user experience, and support secure digital banking.
Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention
The biggest benefit of biometrics in banking is stronger security. Biometric authentication relies on unique biological traits such as fingerprints, facial features, voice patterns, or iris scans. Unlike passwords or PINs, these traits cannot be easily guessed, shared, or stolen.
This greatly reduces risks related to phishing attacks, credential theft, account takeovers, and identity fraud. Biometric security adds a strong layer of protection to online banking, mobile banking apps, and ATM transactions. It plays a critical role in modern financial cybersecurity and fraud prevention strategies.
Faster and Better Customer Experience
Biometrics makes banking easier for customers. Users no longer need to remember complex passwords or answer security questions. A quick fingerprint scan, facial recognition check, or eye recognition process allows instant access to accounts.
This smooth login experience saves time and reduces frustration. Faster authentication improves customer satisfaction, boosts engagement, and encourages users to adopt digital banking services. Simple and secure access is now a key part of customer experience management in banking.
Reduced Operational and Support Costs
Biometric systems automate identity verification. This reduces the number of password reset requests, failed login issues, and customer support calls. Banks can lower operational costs by minimizing manual verification processes.
Fewer security breaches and fraud cases also mean lower financial losses. By improving authentication accuracy, banks protect both their customers and their own resources.
Stronger Regulatory Compliance
Biometric authentication helps banks meet strict regulatory requirements related to data protection and secure access. Many financial regulations require strong customer authentication and identity verification. Biometrics supports compliance by providing reliable and traceable authentication methods.
This makes it easier for banks to follow security standards while maintaining a smooth user experience.
Scalable and Future-Ready Security
Biometric technology is highly scalable. It can be integrated across mobile apps, online platforms, call centers, and physical branches. As banking continues to move toward digital-first models, biometric security systems are future-ready and adaptable.
They support advanced technologies like AI-based fraud detection, multi-factor authentication, and secure digital identity management.
Challenges and Considerations for Biometric Authentication Implementation

Despite the strong advantages, implementing biometric authentication in banking comes with several challenges. Banks must carefully manage data privacy, system performance, and biometric security systems to ensure a safe and reliable rollout.
Privacy Concerns in Biometric Systems
One of the biggest concerns is biometric data privacy. Banks store sensitive information such as fingerprint data, facial recognition data, and iris scan records. If this data is compromised, it cannot be changed like passwords or PINs.
To reduce risk, banks must use end-to-end encryption, secure identity management systems, and GDPR-compliant data protection frameworks. Strong biometric data security is essential to maintain customer trust and meet regulatory requirements.
Accuracy and Reliability Issues
No biometric authentication system is completely flawless. Environmental factors like poor lighting can affect facial recognition accuracy, while noise can impact voice recognition authentication. Physical changes may also interfere with fingerprint scanning or eye recognition systems.
Banks must choose advanced AI-powered biometric verification tools with low false acceptance rates (FAR) and false rejection rates (FRR). High accuracy is critical for secure digital banking authentication and smooth user experience.
Cost of Integration and Infrastructure
The cost of biometric integration can be high, especially for large financial institutions. Expenses include biometric hardware, authentication software, system upgrades, and staff training.
However, when viewed long-term, biometric banking solutions help reduce fraud losses, improve identity verification, and lower operational costs. A well-planned biometric security strategy ensures better ROI and sustainable implementation.
The Future of Your Finances is Biometric

Biometric authentication is no longer a futuristic idea. It is already transforming banking security systems around the world. By using unique biological traits like fingerprints, facial features, and iris patterns, banks can provide a much higher level of protection than traditional password-based authentication and PINs.
This shift plays a major role in strengthening cybersecurity in digital banking. Biometric login systems help prevent identity theft, account takeover fraud, and unauthorized access to online banking platforms. As a result, customer data and financial transactions remain safer from evolving cyber threats.
While challenges such as biometric data privacy, regulatory compliance, and implementation costs still exist, the long-term benefits outweigh the risks. With proper data encryption, secure biometric storage, and compliance with data protection regulations, banks can build trust while improving security.
As financial technology innovation continues to evolve, biometric solutions will become a core part of digital identity verification. The future of banking depends on secure, fast, and user-friendly authentication—and biometrics is leading the way toward a safer financial experience for everyone.
Conclusion
Biometric authentication is rapidly becoming the backbone of modern banking security. As traditional authentication methods like passwords and PINs continue to fail against advanced cyber threats, banks need stronger and smarter solutions. Biometric security systems provide that next level of protection by using unique biological traits that are extremely hard to steal or duplicate.
From fingerprint authentication and facial recognition technology to voice biometrics and iris scanning, banks now have multiple ways to strengthen digital identity verification. These methods not only reduce financial fraud and unauthorized access, but also improve the customer experience in digital banking by making logins faster and simpler.
While challenges like biometric data privacy, regulatory compliance, and implementation costs still exist, they can be managed with data encryption, secure biometric storage, and GDPR-compliant security frameworks. When implemented correctly, biometric authentication supports both financial cybersecurity and long-term customer trust.
Looking ahead, biometric banking solutions will play a central role in secure digital banking, AI-driven fraud prevention, and multi-factor authentication systems. Banks that invest in biometrics today are preparing for a future where security, convenience, and trust go hand in hand.
In short, the future of banking is passwordless, secure, and biometric-powered.
FAQs
What happens if my biometric data is stolen?
If biometric data is stolen, it cannot be changed like a password. This is why banks use advanced encryption and security measures, such as storing data as a template rather than an actual image, to protect it.
Can biometric authentication be fooled?
While it is much harder to fool than traditional methods, no system is completely infallible. However, modern biometric systems often include “liveness detection” to prevent spoofing with photos or recordings, making them highly secure.
Will biometrics replace passwords entirely?
Biometrics are likely to become the primary method of authentication for many banking services. However, passwords and PINs may still be used as a secondary or backup verification method, creating a multi-factor authentication system for even greater security.
Is my phone’s biometric scanner secure enough for banking?
Yes, the biometric scanners on modern smartphones are generally very secure and meet the high standards required by financial institutions. They provide a convenient and safe way to access your banking app.








How AI-Based Fraud Detection is Protecting Digital Payments
Embedded Finance and the Future of Seamless Digital Financial Services
Harnessing AI and Machine Learning for Fraud Detection in Digital Finance
Embedded Finance: How Seamless Financial Services Are Integrating into Everyday Apps
Digital Twin Technology in Finance: How Virtual Models Are Transforming Risk Management
The Future of Personal Finance: Autonomous Finance and AI Money Management
AI Credit Scoring: Revolutionizing SME Banking and Digital Loans
AI Fraud Detection: How Banks Prevent Financial Crime in Real Time